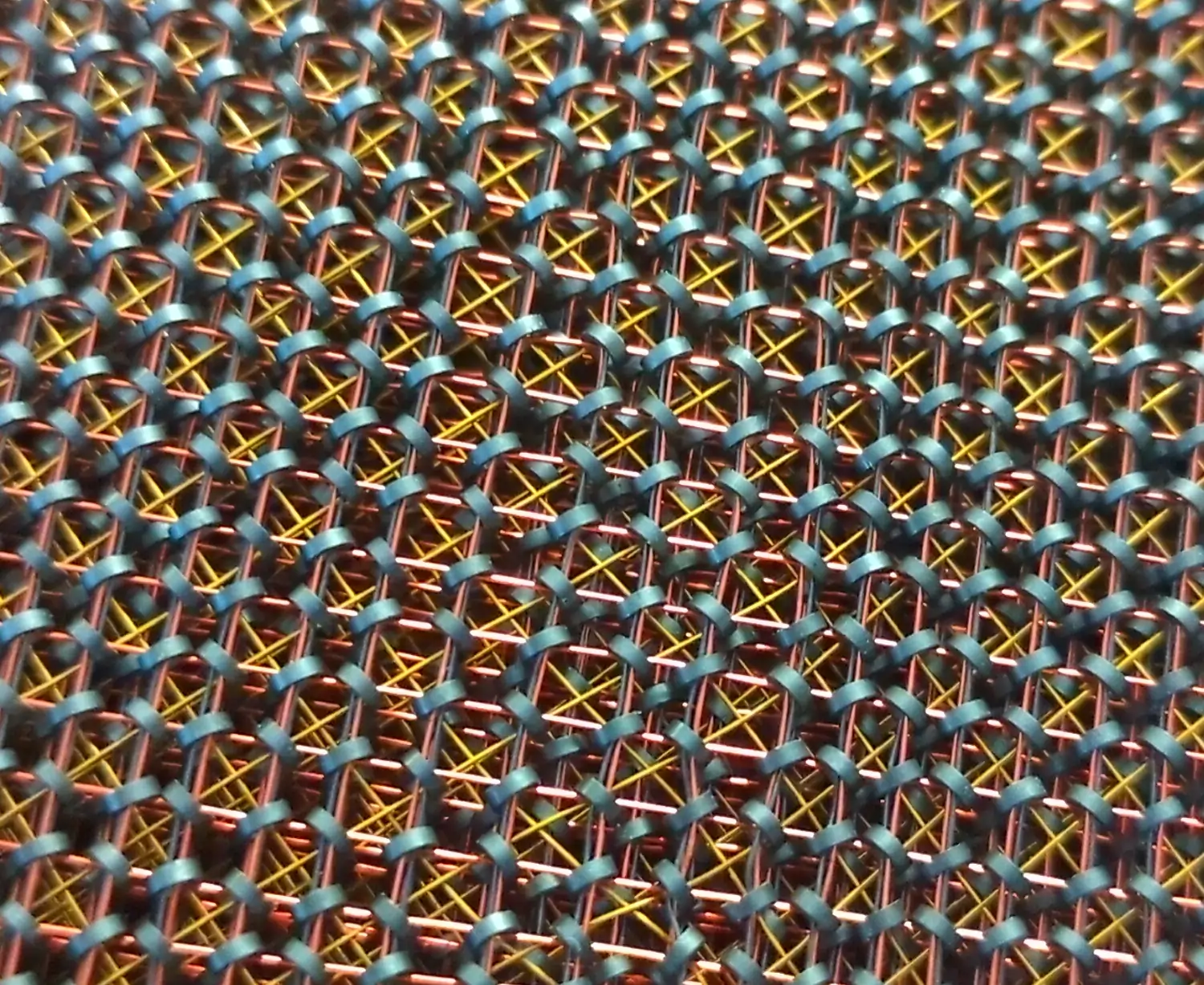
What is Magnetic-core memory?
Core memory uses toroids (rings) of a hard magnetic material (usually a semi-hard ferrite). Each core stores one bit of information. Two or more wires pass through each core, forming an X-Y array of cores. When an electrical current above a certain threshold is applied to the wires, the core will become magnetized. The core to be written is selected by powering one X and one Y wire to half of the required power, such that only the single core at the intersection is written. Depending on the direction of the currents, the core will pick up a clockwise or counterclockwise magnetic field, storing a 1 or 0. This writing process also causes electricity to be induced into nearby wires. If the new pulse being applied in the X-Y wires is the same as the last applied to that core, the existing field will do nothing, and no induction will result. If the new pulse is in the opposite direction, a pulse will be generated. This is normally picked up in a separate "sense" wire, allowing the system to know whether that core held a 1 or 0. As this readout process requires the core to be written, this process is known as destructive readout, and requires additional circuitry to reset the core to its original value if the process flipped it.